Summary
Objective : Evaluate the treatment effectiveness of the Qi Gong nourishes health practice method and some related factors in post-COVID-19 treatment. Research method : Clinical intervention, before-after comparison of treatment on 121 patients with post-COVID-19 disorders according to modern medicine and belongs to the Lung and Spleen qi deficiency of traditional medicine, came for examination and treatment. treatment at the National Hospital of Acupuncture from March to October 2023. Patients can practice Qi Gong nourishes health Nguyen Van Huong exercise once a day, 30-45 minutes each time. Evaluation criteria include dyspnea (mmrc scale), fatigue (Borg-CR scale), quality of life score (EQ-5D-5L scale) on days D0, D15 and D30 after treatment. The collected data are processed using SPSS 20.0, the difference is statistically significant when p < 0.05. The study complied with 13 principles of biomedical ethics. Results: Excellent and good effectiveness 68.6%. Clinical symptoms of modern medicine and traditional medicine improved statistically significantly compared to the time before treatment (p<0.05), quality of life score EQ-5D-5L excellent reached 39.7 %; good reached 43%; 17.3% Average; The level of shortness of breath gradually improved, the effectiveness after treatment reached excellent 30.5%; good 57%; Average 12.4%; Fatigue level improved excellently, effectiveness after treatment reached 81.8% excellent; 16.5% good and 1.7% Average. Conclusion : Nguyen Van Huong's Qi Gong nourishes health practice method is excellently effective in improving post-COVID-19 disorders of the Lung and Spleen qi deficiency.
I. INTRODUCTION
Post-COVID-19 syndrome occurs when symptoms of the acute phase persist after 4 weeks from the first symptom onset. due to infection with the Sars-CoV-2 virus. Reports of post-COVID-19 symptom rates range from 32.6% to 87% of hospitalized patients. For subjects with COVID-19 who were not hospitalized and had post-COVID-19 symptoms, 37% had fatigue and 30% had cognitive impairment. Other less typical symptoms include mental confusion, headache, muscle pain, chest pain, joint pain, olfactory and taste dysfunction, cough, hair loss, insomnia, wheezing, and watery discharge nose, phlegm, cardiovascular and gastrointestinal problems. These symptoms can last up to six months from hospital discharge or symptom onset, but in many cases the symptoms last longer, affecting their quality of life.
Patients with negative COVID-19 treatment encounter many cases that leave serious sequelae, the most serious being respiratory function. To treat COVID-19 comprehensively, especially improving lung function and psychological stability, enhancing mobility, and preventing both physical and mental decline. The goal of the health sector is to control and find effective measures to prevent this disease, especially the symptoms of cough and shortness of breath . In addition, traditional medicine also contributes significantly to the treatment and recovery of post-COVID 19 patients such as drinking traditional medicine decoctions and non-drug methods such as acupuncture, thread implantation, and Qi Gong exercises. nourishes health ... In particular, the Qi Gong nourishes health practice method is mentioned in diseases of the respiratory tract, musculoskeletal system, digestive system..., and in fact at the National Hospital of Acupuncture, the Qi Gong nourishes health method has been applied. In treating post-COVID-19 patients, many clinical results have been achieved, but there have not been many reviews on the effects of Qi Gong nourishes health treatment on post-COVID-19.
II. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
Evaluating the effectiveness of post-COVID-19 treatment of Lung and Spleen qi deficiency using the Qi Gong nourishes health practice method and some related factors.
III. RESEARCH SUBJECTS & METHODS
Study subjects: Convenience sample of 121 patients diagnosed with post-COVID-19 disorder according to the Ministry of Health's guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of post-COVID-19 infection in adults and has clinical symptoms consistent with Lung, Spleen, and Qi Deficiency according to traditional medicine, comply with the treatment process.
|
Modern medicine |
Traditional medicine |
|
(1) Fatigue lasting >12 weeks affects the patient's health and daily activities (2) The following symptoms: - Fatigue increases with exertion and does not decrease with rest - Restless sleep - Impaired memory or ability to concentrate - Headache - Muscle or joint pain but the joint is not swollen, hot, or red - Sore throat or mouth ulcers - Swollen and painful lymph nodes (armpit, neck) |
- Afraid of cold, white face. - Shortness of breath. - Dry cough or prolonged cough. - Sore throat, possible loss of smell. - Pale tongue, white moss. - Weak pulse.
|
Research time and location: National Hospital of Acupuncture, from March to October 2023.
Research design: Prospective clinical intervention, comparison before and after treatment.
Method for evaluating results
Table 1. Outcome assessment tools
|
Category |
Tools |
Level |
Efficiency improved |
|
Life quality |
EQ-5D-5L |
1-very high; 2-high; 3-medium; 4-low; 5-very low |
≥75%= excellent ; 50-75%=good; 25-<50%= Average ; <25%=poor |
|
Shortness of breath |
mMRC |
no dyspnea, mild dyspnea, moderate dyspnea, severe dyspnea and very severe dyspnea |
|
|
Tired |
Borg-CR |
Not tired, mildly tired, moderately tired, very tired, very tired |
Data processing: Data obtained in the study were analyzed and processed according to biomedical statistical methods, using SPSS 20.0 software.
Research ethics: Adhere to biomedical ethical principles.\
IV. RESEARCH RESULTS
Of the 121 patients participating in the study, 47.9% were 60 years old or older; 39.7% from 40-<60 years old; 12.4% from 18-<40 years old; male accounts for 57.9%; 86.8% had normal BMI ; 89.3% of patients have received 2 doses of COVID-19 vaccine. The improvement in dyspnea and fatigue levels is shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Effectiveness in improving levels of shortness of breath and fatigue
|
Point ladder |
Excellent |
Good |
Average |
poor |
||||
|
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
n |
% |
|
|
mMRC assesses dyspnea |
37 |
30.5 |
69 |
57.0 |
15 |
12.4 |
0 |
0 |
|
Borg-CR fatigue assessment |
99 |
81.8 |
20 |
16.5 |
2 |
1.7 |
0 |
0 |
|
EQ-5D-5L assesses quality of life |
48 |
39.7 |
52 |
43 |
21 |
17.3 |
0 |
0 |
The levels of shortness of breath, fatigue and quality of life scores all changed excellently after treatment. The proportion of patients with excellent and good results is higher than the average and poor groups.
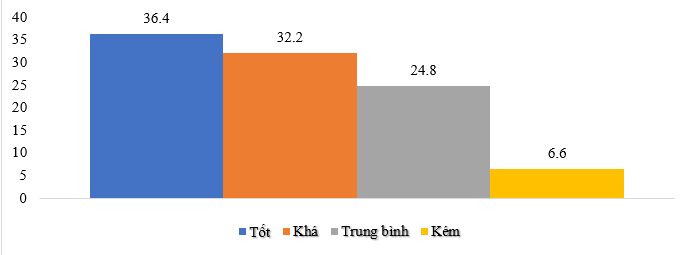
The percentage of patients with excellent and good results is high, 68.6% respectively.
Table 3. Some factors related to treatment results
|
Related factors |
Treatment results (n,%) |
p |
||||
|
Excellent |
Good |
Average |
Inefficient |
|||
|
Age group |
< 40 years old |
14 (93.3) |
1 (6,7) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
<0.05 |
|
≥ 40 years old |
30 (28.3) |
38 (35.8) |
30 (28.3) |
8 (7.6) |
||
|
Sex |
Female |
21 (41.1) |
25 (49.0) |
3 (5.9) |
2 (4.0) |
>0.05 |
|
Male |
23 (32.9) |
14 (20.0) |
27 (38.6) |
6 (85) |
||
|
BMI |
BMI ≤ 23 |
43 (39.8) |
37 (34.3) |
27 (25.0) |
1 (0.9) |
<0.05 |
|
BMI >23 |
1 (7.7) |
2 (15.4) |
3 (23.1) |
7 (53.8) |
||
|
Number of COVID shots |
1 nose |
2 (15.3) |
1 (7.7) |
5 (38.5) |
5 (38.5) |
<0.05 |
|
≥ 2 shots |
42 (38.9) |
38 (35.2) |
25 (23.1) |
3 (2.8) |
||
|
EQ-5D-5L assesses quality of life |
Very high |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
<0.05 |
|
High |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
||
|
Medium |
40 (39.2) |
34 (33.3) |
27 (26.5) |
1 (1.0) |
||
|
Short |
3 (27.3) |
5 (45.5) |
1 (9.1) |
2 (18.1) |
||
|
Very low |
1 (12.5) |
0 (0) |
2 (25.0) |
5 (62.5) |
||
|
mMRC assesses dyspnea |
No difficulty breathing |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
<0.05 |
|
Mild shortness of breath |
40 (90.9) |
4 (9.1) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
||
|
Moderate shortness of breath |
3 (8.8) |
31 (91.2) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
||
|
Severe difficulty breathing |
1 (3.7) |
4 (14.8) |
19 (70.4) |
3 (11.1) |
||
|
Very severe difficulty breathing |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
11 (68.8) |
5 (31.2) |
||
|
Borg-CR fatigue assessment |
Not tired |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
<0.05 |
|
Mild fatigue |
20 (87.0) |
2 (8.7) |
1 (4,3) |
0 (0) |
||
|
Moderate fatigue |
23 (25.0) |
37 (40.2) |
25 (27.2) |
7 (7.6) |
||
|
Very tired |
1 (16.7) |
0 (0) |
4 (66.6) |
1 (16.7) |
||
|
Very tired |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
||
Factors like age, BMI, number of vaccinations, quality of life scores, breathlessness and fatigue levels were different after treatment (p<0.05).
V. DISCUSSION
Qi Gong nourishes health practice is an effective mechanical therapy method of traditional medicine, easy to perform, not complicated movements, patients can do it themselves at home, widely used in treatment, disease prevention, and health recovery. Practicing Qi Gong nourishes health to help increase the differentiation process, reorganize the patient's brain and significantly reduce secondary injuries. The clinical symptoms improved significantly, which is also the basis for the scores to show excellent effectiveness in intervention with Qi Gong nourishes health exercises for the selected disease. This is further evidenced by the overall treatment results, the percentage of patients with excellent and good results is high, 68.6% respectively. Only 24.8% of patients had Average treatment effectiveness and 6.6% of patients had ineffective treatment.
Factors like age, BMI, number of vaccinations, quality of life scores, breathlessness and fatigue levels were different after treatment (p<0.05). The results of this study are similar to some domestic and foreign authors such as: Nguyen Van Thao recorded factors such as age, gender, place of residence, body mass index, vaccination against COVID-19, and disease. Patients with a history of previous severe COVID-19 infection and underlying diseases related to post-COVID-19 neurological complications. Zhang X and colleagues noted that age, gender, and severity of Covid-19 infection were related to neurological complications. As well as authors Pilotto A et al and authors Nashwa Radwan and colleagues noted neurological complications in post-COVID-19 patients related to age, gender, severity of COVID-19 infection and comorbidities. Mohammed Samannodi showed that age was a significant predictor of post-COVID-19 conditions, especially in the age group 60 years and older with a 1.5-fold increased risk of post-COVID-19 symptoms ( 95% confidence interval: 1.13-1.99) compared to younger age groups.
VI. CONCLUDE
Nguyen Van Huong's Qi Gong nourishes health practice method is excellently effective in improving post-COVID-19 disorders such as lung, spleen and qi deficiency.
Keyword
Post-COVID-19,Lung and Spleen qi deficiency,Qi Gong nourishes health
References
- Nguyen Van Thao, Nguyen Van Khoe, Ngo Hoang Toan and colleagues. Research on the situation and factors related to neurological complications in post-COVID-19 patients at Kien Giang general hospital in 2022-2023. Can Tho Journal of Medicine and Pharmacy . 61/2023, 142-147.
- Khue NNN, Hau VTQ, Khoa NA, Phuc L, Huyen NH. Post-COVID-19 characteristics in Dak Lak, 2022. VMJ. 2022; 513(1). doi:10.51298/vmj.v513i1.2362
- Lopez-Leon S, Wegman-Ostrosky T, Perelman C, et al. More than 50 Long-term effects of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. medRxiv. Published online January 30, 2021:2021.01.27.21250617. doi:1 0.1101/2021.01.27.21250617.
- Zhang X, Wang F, Shen Y et al. Symptoms and health outcomes among survivors of Covid-19 infection 1 year after discharge from hospitals in Wuhan, China. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. 4(9), e2127403, doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.27403.
- Samannodi M, Alwafi H, Naser AY, Al Qurashi AA, T. Qedair J, et al. Determinants of PostCOVID-19 Conditions among SARS-CoV-2-Infected Patients in Saudi Arabia: A Web-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Diseases . 2022. 10 (3), doi: 10.3390/diseases10030055.
- Nalbandian A.; Sehgal K.; Gupta A; (2021), "Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome", Med . 27, p. 601–615.
- SF Farhadian, D. Seilhean and S. Spudich (2021), "Neuropathogenesis of acute coronavirus disease 2019", Curr Opin Neurol . 34(3), p. 417-422.
